Technical White Paper
In the past decade, the blockchain has evolved from a geek concept that exists only in small circles to a concept that is widely understood and accepted by the public. Blockchain technology has also experienced several stages in this period of time:
-
The blockchain represented by Bitcoin can be summarized as the first generation. The main feature of its function is to support the decentralized token payment system. The
Proof of Workis the core consensus mechanism, and the speed of transaction confirmation is tens of minutes. -
Blockchain represented by Ethereum can be called the second generation. Its main feature is to support
Turing-Completesmart contract system. The speed of transaction confirmation is minutes which is improved compared with the previous generation. -
EOS represents the third-generation blockchain technology. By improving the consensus mechanism (
Proof of Stake) and enhancing scalability, the confirmation speed and throughput efficiency of blockchain transactions are greatly improved.
Based on the third-generation EOS, HOT builds the underlying system, inherits all the technical advantages of EOS, and makes improvements to HOT applications.
Technical Features
C++/WASM Virtual Machine
HOT builds the underlying system based on EOSIO, and makes improvements according to the bussiness characteristics of HOT.
For EOSIO, it uses C++ as the smart contract programming language. Given C++ is a popular programming language among developers around the world, any developer who is familiar with C++ is not required to learn a new programming language to pick up EOSIO’s APIs, which will be covered in this onboarding series. Once familiarity with EOSIO’s APIs has been achieved, a developer will be able to program EOSIO smart contracts using canonical C++ code constructs.
On top of EOSIO core layer, a WebAssembly (WASM) virtual machine executes smart contract code. The design choice of using WASM enables HOT to re-use optimized and battle-tested compilers and toolchains which are being maintained and improved by a broader community.
High Throughput and Scalability
HOT is designed for achieving high transaction throughputs. Using the consensus mechanism of Delegated Proof of Stake (DPOS), an HOT blockchain network does not need to wait for all nodes to complete a transaction to achieve finality. This enables much higher transaction throughput when compared to other consensus mechanisms.
Faster Confirmations and Lower Latency
To facilitate good user experience, HOT is designed to have low latency for transaction confirmation so that applications built by developers can compete with non-blockchain, centralized, alternatives.
Feeless and Cost Predictable Blockchain
Applications built on HOT can adopt a freemium model in which users are not required to pay for the cost of infrastructure. A user does not have to pay a fee to transact. HOT blockchains are unique in that the infrastructure resource is regulated by a staking mechanism. Infrastructure resource is based on token staked in ratio to the total available resource and is fixed once tokens have been staked.
Comprehensive Permission Schema
HOT has a comprehensive permission system for creating custom permission schema for various use cases. This comprehensive permission system allows developers to build a permissioned application on top of a flexible infrastructure without having to reinvent the wheel.
Upgradability
Applications deployed on HOT based blockchains are upgradeable. This means developers can deploy code fix, add features, and/or change application logic, as long as sufficient authority is provided. As a developer, you can iterate your application without the risk of being locked-in to a mistake or bug permanently. It is also possible, however, to deploy smart contracts that cannot be modified on HOT based blockchains. These decisions are at the discretion of developers rather than restricted by the protocol.
Less energy consumption
With DPOS as the consensus mechanism, HOT consumes much less energy to validate transactions and secure a blockchain compared to other consensus algorithms
Programmable Economics and Governance
The resource allocation and governance mechanism of any HOT based blockchain are programmable via smart contracts. Developers only need to modify the system smart contracts to change resource allocation and governance rules of an HOT blockchain.
HOT, Rooted in the system contract
The issuance of HOT tokens is achieved through system contract, which is ensuring openness and fairness. All logical changes at the system contract level need to be completed based on HOT’s governance mechanism to ensure the transparency and democracy of system.
Stack
Smart Contract/CDT
HOT.CDT is a toolchain for WebAssembly (WASM) and set of tools to facilitate contract writing for the HOT platform. In addition to being a general purpose WebAssembly toolchain, HOT specific optimizations are available to support building HOT smart contracts. This new toolchain is built around Clang 7, which means that HOT.CDT has the most current optimizations and analyses from LLVM. However, as the WASM target is still considered experimental, some optimizations are not available or incomplete.
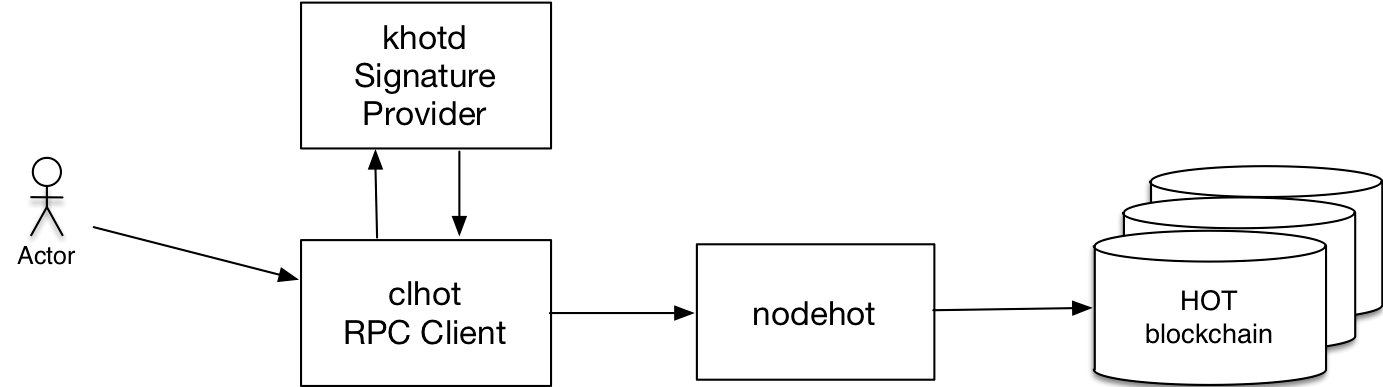
NodeHot
NodeHot is the core HOT node daemon. Plugins can be used to configure NodeHot to execute with various features. NodeHot handles all peer-to-peer networking, contract code scheduling, and the blockchain data persistence layer. For development environments, NodeHot can also be used to set up a single node blockchain network.
Clhot / Khotd
Khotd is a key manager for HOT accounts that comes with HOT.
Clhot is a command-line tool which let developers interact NodeHot as well as deploy, test HOT smart contracts.